On-Page SEO – A Practical Guide
On-Page SEO* (or on-site SEO) is the practice of altering a page’s content in order to improve its search engine rankings on a given keyword. The optimization process includes adding keywords to the page’s content, writing meta tags, image optimization and more.
*As opposed to off-page SEO, which focuses on the marketing activities taken outside the website, such as link building, social media marketing, etc.

What is the real impact of on-site SEO on Google’s rankings?
Despite’s Google’s frequent algorithm updates, AI systems and other changes, on-site SEO still has a significant impact on search results rankings. And even Google admits it: “The most basic signal that information is relevant is when a webpage contains the same keywords as your search query. If those keywords appear on the page, or if they appear in the headings or body of the text, the information is more likely to be relevant.” (From How Search algorithms work).
This claim is also supported by several researches from recent years:
- A survey taken by SEMrush about the ranking factors showed that the keyword appears in 75% of the pages in the 20 top organic results, and in 60% of them, the keyword also appears in the title tag.
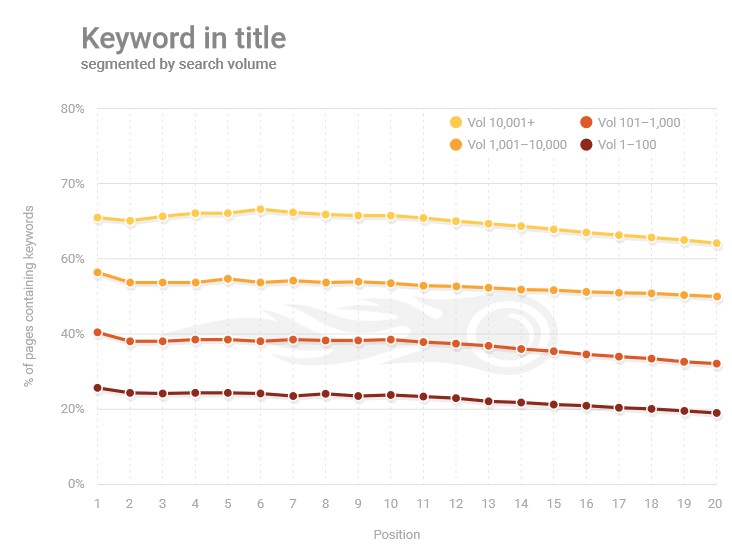
- Another finding from the survey showed that in high-volume keywords, the exact term is found in both the content and the meta tags. In long-tail keywords, the on-page SEO elements were less present, and also less essential.
- According to a similar survey by MOZ, the placement of the keywords in the title impacts the page’s ranking. In other words, when a keyword is placed in the beginning of the sentence – it will usually rank higher.
The on-page SEO elements can be divided into three categories:
Code – including meta tags, headings, images alt tags and schema tags.
Content – mainly the integration of the keywords in the content body and headings, optimizing the content to the users’ intention.
Architecture – optimization of the URLs, menus and internal links.
Additional ranking factors that can be linked to on-page SEO include page speed, mobile optimization, website’s reputation and users’ behavior.
On-Page SEO Guidelines
Meta Tags – Titles & Descriptions for SEO
The meta tags (i.e. meta title and meta description) are important ranking factors, and also the easiest to implement.
The title helps both Google and users to understand the page’s content, and it is considered a key ranking factor.
The description may not influence rankings directly (and Google even announced it back in 2009). In addition, Google is not obligated to display the meta description in the search results, and in many searches you will see a different snippet than the one specified in the meta tag. However, the meta descriptions can impact click-through rate (CTR), and by that – impact Google’s ranking. That’s why, it is usually advised to invest in unique descriptions instead of letting Google to choose a random snippet from the page’s content.
Checklist for SEO-Friendly Meta Tags:
- A unique title & description to each page.
- The main keyword appears in the beginning of the title.
- The secondary keywords or synonyms are integrated naturally in the title and description.
- You use click-baiting adjectives in the titles (such as new, the latest, the best, the most comprehensive….).
- You avoid composing the title and description from an incoherent list of too many keywords and variations of the main keywords. For example: Payday Loan | Online Loan | Get Pay Payday Loans
- The titles are not longer than 60 characters (including the brand’s name), and the descriptions – about 160 characters.
Headings
The headings in the content body itself also play a role in content optimization, as well as improving its accessibility and usability. Similar to the title tag, a keyword-rich headline can help Google understand the content subject. Subheadings also help users to scroll the content. Headings can also improve rankings in long-tail keywords and in People Also Search results.
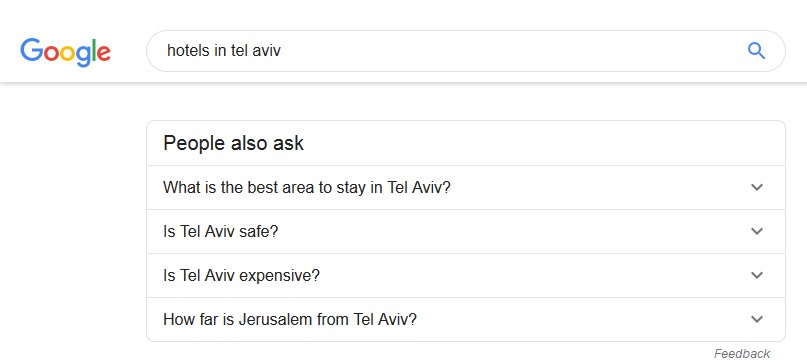
Checklist:
- One headline (H1) per page.
- The main keyword appears in the headline and at least in one subheading.
- The secondary keywords appear in the subheadings.
- The subheadings (and preferably all the headings) use natural language and questions.
Image Optimization Checklist
- All images have alt and title tags, including logos and other graphic elements.
- The alt and title tags integrate the relevant keywords to the image and general context of the page.
- The tags are no longer than 100-120 characters.
- The keywords density makes sense.
Schema Tags (Structured Data)
Similar to the meta-description tag, the schema tags (to highlight structured data) don’t improve ranking directly. Also there’s no guarantee from Google’s side that implementing these tags will impact the search appearance. But, if it will, rich results can have a positive impact on the CTR, especially in types of content such as products, recipes, events, local businesses, as well as articles and blog posts.
Content
It’s true that keyword density belongs to the old world of SEO. Still, if the target keyword doesn’t appear in the content at least once, how will Google be able to match it to the search query?
Checklist
- The main keyword appears several time in the content body, and at least once in the opening paragraph.
- The secondary keywords, synonyms and extensions of the main keyword are all distributed in the content body in a natural and sensible way.
- The content answers the target search queries and matches the relevant user’s intent
For example, if the user searched for a product, let’s say a laptop, the intent is probably transactional, and the matching content should be a product or a category page, and not an article about the technology of laptops.
- The author’s name and expertise are highlighted.
- Original, comprehensive and interesting content (obviously).
Website Architecture
URL address
A textual URL address is another way to describe the page’s content. It’s easier for Google to understand URL addresses such as example.com/key-phrase than pages like example.com/?p1233. It’s also easier for users to remember these pages, reach them and link to them.
- The essence of the page’s content (=the main keyword) appears in the URL, i.e. without linking words, truncated sentences, and obviously – without too many keywords.
- The page’s location in the website’s hierarchy is reflected in the URL.
For example:
example.com/services/seo
example.com/product-category/product-sub-cateogry/product-page
Internal Keywords
Internal keywords help SEO in several ways: they help Google to discover new content and to understand the website’s content and hierarchy. In addition, internal links can help users to prolong the users’ dwelling time, and by that send Google the message that the website is relevant to the search query and is worthy of high rankings.
- The most important pages (category pages, products or services pages, and even blog posts) will be linked from the menus and navigation bars, as well as contextual links.
- Additional ways to add internal links include features such as similar posts (or similar products/people also bought if it is an ecommerce site).
- Ideally, there won’t be any orphaned, unlinked pages (of course, depending on the website’s size).
- The anchor text (link text) will include the relevant keywords for the linked page (again, reasonably).
Additional ways to prolong dwelling time:
- Display a summary of the page above the fold.
- In long-form content, also add a table of content with in-page links.
- Display the content in a format that enables quick scrolling: short paragraphs, sub-headings, bulleted or numbered lists, images and videos.
- Improve the page’s speed.
Page speed can be tested using tools such as Google’s Pagespeed Insights, Pingdom or GTmetrix.
By crawling the website, using tools such as Screaming Frog, you can discover common on-site SEO errors such as missing Meta Descriptions, duplicate Meta Titles, missing H1, etc.
To summarize, on-page SEO (and SEO in general) is not a one-time activity, but something you should check and update regularly.
Need help? Contact us.